Off-Grid Residential Solar Power System: Configuration, Pricing, and Benefits
As the demand for clean and sustainable energy grows, off-grid residential solar power systems have become an increasingly popular choice for homeowners seeking energy independence. These systems allow households to generate and store their own electricity, making them ideal for remote areas without access to the grid or for those who want to reduce their reliance on traditional energy sources. This article will provide a comprehensive guide to off-grid residential solar power systems, including configuration options, pricing, and benefits.
1. What is an Off-Grid Residential Solar Power System?
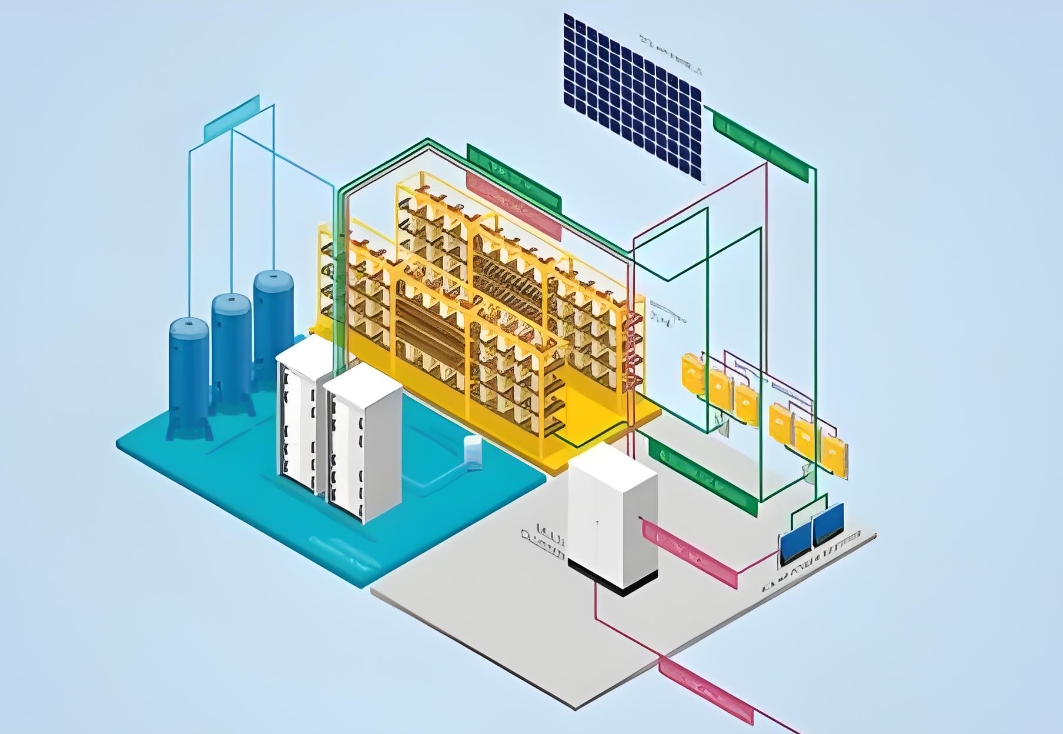
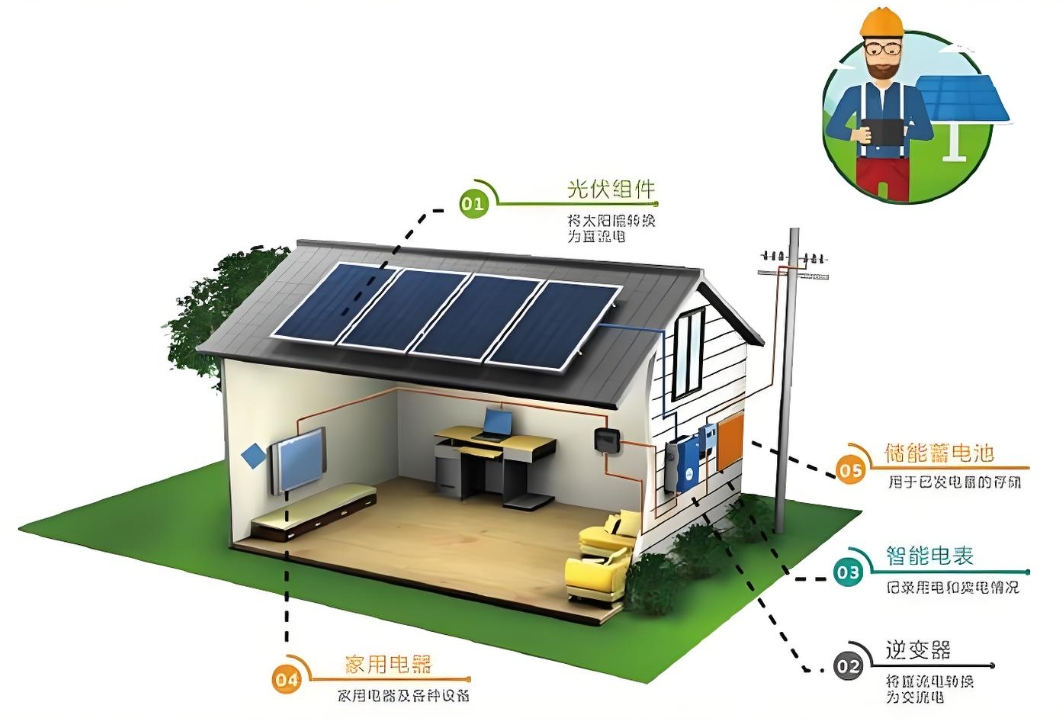
An off-grid solar power system is a self-sufficient energy solution that generates electricity from solar panels and stores it in batteries for later use. Unlike grid-tied systems, off-grid systems operate independently of the utility grid, making them suitable for remote locations or areas with unreliable grid access.
Key Components of an Off-Grid Solar System:
1. Solar Panels: Convert sunlight into electricity.
2. Battery Bank: Stores excess energy for use during nighttime or cloudy days.
3. Charge Controller: Regulates the flow of electricity from the solar panels to the batteries.
4. Inverter: Converts DC electricity from the batteries into AC electricity for household appliances.
5. Backup Generator (Optional): Provides additional power during extended periods of low sunlight.

2. Configuration Options for a Residential Off-Grid Solar System
The configuration of an off-grid solar system depends on the household's energy consumption, location, and budget. Below is a detailed configuration for a typical residential off-grid solar system.
2.1 Energy Consumption Assessment
Before designing the system, it is essential to calculate the household's daily energy consumption. For example:
- Lighting: 5 hours/day × 100W = 500Wh
- Refrigerator: 24 hours/day × 150W = 3,600Wh
- TV: 4 hours/day × 100W = 400Wh
- Water Pump: 2 hours/day × 500W = 1,000Wh
- Other Appliances: 1,000Wh
- Total Daily Consumption: 6,500Wh (6.5KWh)
2.2 Solar Panel Array
- Daily Energy Requirement: 6.5KWh
- Sunlight Hours: Assume 5 peak sunlight hours per day.
- System Efficiency: Account for 80% efficiency due to losses.
- Required Solar Panel Capacity: 6.5KWh ÷ 5 hours ÷ 0.8 = 1.625KW (1,625W)
- Recommended Solar Panels: 8 × 300W panels (2.4KW total capacity to account for cloudy days).
2.3 Battery Bank
- Daily Energy Requirement: 6.5KWh
- Days of Autonomy: 3 days (to ensure power during extended cloudy periods).
- Battery Depth of Discharge (DoD): 50% (to extend battery life).
- Required Battery Capacity: 6.5KWh × 3 ÷ 0.5 = 39KWh
- Recommended Batteries: 8 × 5KWh lithium-ion batteries (40KWh total capacity).
2.4 Charge Controller
- Solar Panel Capacity: 2.4KW
- Battery Voltage: 48V (common for residential systems).
- Charge Controller Rating: 2,400W ÷ 48V = 50A
- Recommended Charge Controller: 60A MPPT charge controller (to handle peak current).
2.5 Inverter
- Total Load: Assume a peak load of 3KW.
- Recommended Inverter: 5KW pure sine wave inverter (to handle surges and ensure stable power output).
2.6 Backup Generator (Optional)
- Capacity: 5KW diesel or propane generator.
- Usage: For extended periods of low sunlight or high energy demand.
3. Pricing of an Off-Grid Residential Solar System
The cost of an off-grid solar system depends on the components' quality, capacity, and brand. Below is a price breakdown for the above configuration.
3.1 Solar Panels
- 300W Solar Panels: $150 per panel.
- Total Cost: 8 × $150 = $1,200.
3.2 Battery Bank
- 5KWh Lithium-Ion Batteries: $1,500 per battery.
- Total Cost: 8 × $1,500 = $12,000.
3.3 Charge Controller
- 60A MPPT Charge Controller: $300.
3.4 Inverter
- 5KW Pure Sine Wave Inverter: $1,000.
3.5 Backup Generator (Optional)
- 5KW Diesel Generator: $1,500.
3.6 Installation and Accessories
- Mounting Hardware, Wiring, and Labor: $2,000.
3.7 Total System Cost
- Without Generator: $1,200 + $12,000 + $300 + $1,000 + $2,000 = $16,500.
- With Generator: $16,500 + $1,500 = $18,000.
4. Benefits of an Off-Grid Residential Solar System
4.1 Energy Independence
Off-grid systems allow homeowners to generate their own electricity, reducing reliance on the utility grid and protecting against power outages.
4.2 Environmental Impact
Solar energy is clean and renewable, significantly reducing carbon emissions and environmental pollution.
4.3 Cost Savings
While the initial investment is high, off-grid systems eliminate monthly electricity bills and provide long-term savings.
4.4 Remote Accessibility
Off-grid systems are ideal for remote areas where grid connection is impractical or expensive.
4.5 Low Maintenance
Modern solar systems require minimal maintenance, with most components lasting 10-25 years.
5. Market Trends and Future Outlook
5.1 Declining Costs
The cost of solar panels and batteries has decreased significantly over the past decade, making off-grid systems more affordable.
5.2 Technological Advancements
Improvements in battery technology (e.g., lithium-ion, solid-state) and solar panel efficiency are enhancing system performance and reliability.
5.3 Government Incentives
Many governments offer tax credits, rebates, and subsidies to encourage the adoption of solar energy.
5.4 Growing Demand
As awareness of climate change and energy security increases, more homeowners are turning to off-grid solar solutions.
6. Conclusion
An off-grid residential solar power system is a reliable and sustainable energy solution for homeowners seeking energy independence. By carefully designing the system based on energy needs and location, households can enjoy clean, reliable, and cost-effective electricity. While the initial investment may be significant, the long-term benefits—such as reduced energy bills, environmental protection, and energy security—make it a worthwhile investment.
With advancements in technology and declining costs, off-grid solar systems are becoming more accessible and efficient. Whether for remote locations or urban homes, off-grid solar power is paving the way for a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.