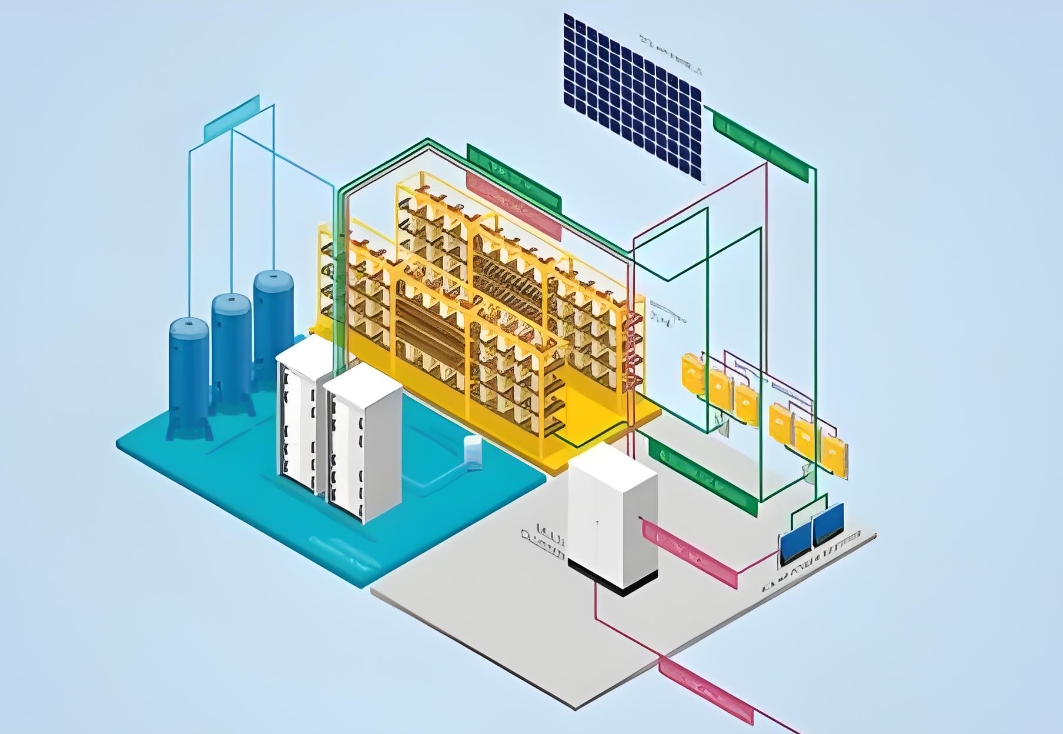
battery energy storage solutions bess
Battery Energy Storage Solutions (BESS) represent a cutting-edge approach to energy management, offering a range of benefits that address modern energy challenges. BESS systems utilize rechargeable batteries to store energy for later use, providing a flexible and reliable source of power that can be integrated into various applications, from residential to industrial and grid-scale operations. Here's an expanded discussion on BESS:
What is BESS?
BESS, or Battery Energy Storage Systems, are energy storage solutions that consist of large-scale batteries housed in containers. These systems can store and release electrical energy as needed, serving as a buffer between renewable energy sources (like solar and wind) and the grid. BESS plays a crucial role in facilitating the integration of renewable energy into the grid, ensuring reliable and stable power supply while providing low-cost, low-carbon electricity.
Key Components of BESS
Hardware Components:
Batteries: The core of any BESS system, individual battery cells store energy through electrochemical reactions. Lithium-ion batteries are commonly used due to their high energy density and long lifespan.
Modules and Battery Packs: Batteries are combined into modules and further integrated into larger battery packs to achieve the desired energy capacity and power output.
Power Conversion System (PCS): PCS converts the direct current (DC) from the batteries into alternating current (AC) compatible with the grid or other loads.
Software Components:
Battery Management System (BMS): BMS monitors and manages the health and performance of the batteries, ensuring safe and efficient operation by preventing overcharging, over-discharging, and other potential hazards.
Energy Management System (EMS): EMS optimizes the operation of BESS by considering grid conditions, energy prices, and user preferences. It intelligently controls the charging and discharging of batteries to maximize energy efficiency and cost savings.
Grid Management System (GMS): GMS facilitates the interaction between BESS and the grid, ensuring seamless integration and operation.
Data Analysis Systems: These systems collect and analyze data from BESS and external systems, providing insights into system performance, energy consumption trends, and potential issues. These data are used for system optimization, maintenance planning, and regulatory compliance.
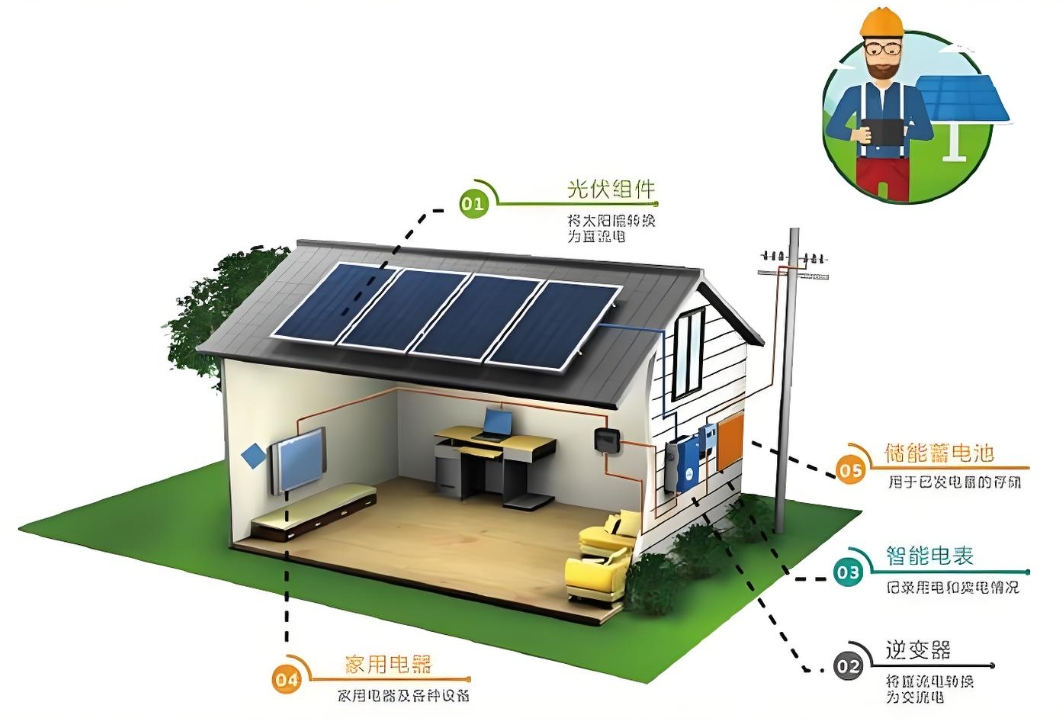
Applications of BESS
Commercial Use:
BESS is deployed in commercial settings for various purposes, such as load shifting, peak shaving, and load flattening. By charging batteries during off-peak hours or when renewable energy is abundant, businesses can reduce their reliance on the grid during peak demand periods, lowering energy costs and minimizing peak kW consumption.
Industrial Applications:
In industrial settings, BESS plays a critical role in energy conservation, emission reduction, and grid stability. It supports the integration of renewable energy into industrial processes, promoting sustainability and reducing carbon emissions.
Grid-Scale Operations:
At the grid level, BESS is essential for ensuring stable and reliable energy systems. It addresses the intermittency of renewable energy by storing excess power generated during high production periods and releasing it during peak demand or low renewable energy output times. This supports the integration of more renewable energy into the grid and enhances the overall efficiency and resilience of the national electricity grid.
Benefits of BESS
Cost Savings:
BESS enables businesses to save costs through load shifting and peak shaving strategies. By purchasing and storing electricity at low prices and using it during peak demand periods, businesses can reduce their electricity bills and even sell stored power at higher rates.
Emission Reduction:
By optimizing the use of renewable energy, BESS helps businesses reduce their dependence on fossil fuels, thereby lowering greenhouse gas emissions. This contributes to achieving internal sustainability goals and aligning with broader national and global environmental objectives.
Energy Security:
BESS provides businesses with greater energy price security and independence. In an era of volatile energy prices and potential grid instability, having a dedicated energy storage system means businesses can maintain operations during price spikes or grid failures, ensuring operational continuity.
Challenges in Implementing BESS
Technical Challenges:
Battery lifespan, efficiency, and performance degradation over time are significant technical challenges. Battery systems' efficiency decreases with repeated charging and discharging cycles, leading to reduced storage capacity and effectiveness.
Economic Considerations:
The initial investment in BESS can be substantial, including costs for batteries, related hardware, installation, and integration into existing power systems. While long-term cost savings and benefits exist, the upfront cost can be a barrier for many businesses and residential users.
Regulatory and Policy Environment:
Navigating the regulatory and policy landscape is another challenge. Policies related to energy storage, grid integration, and renewable energy subsidies are constantly evolving. Successful implementation of BESS requires staying informed and compliant with these regulations, which can significantly impact the economic feasibility of investing in BESS.
In conclusion, Battery Energy Storage Solutions (BESS) offer a versatile and innovative approach to energy management, addressing modern energy challenges while providing a range of benefits. By understanding the key components, applications, benefits, and challenges of BESS, businesses and individuals can make informed decisions about incorporating these systems into their energy strategies.