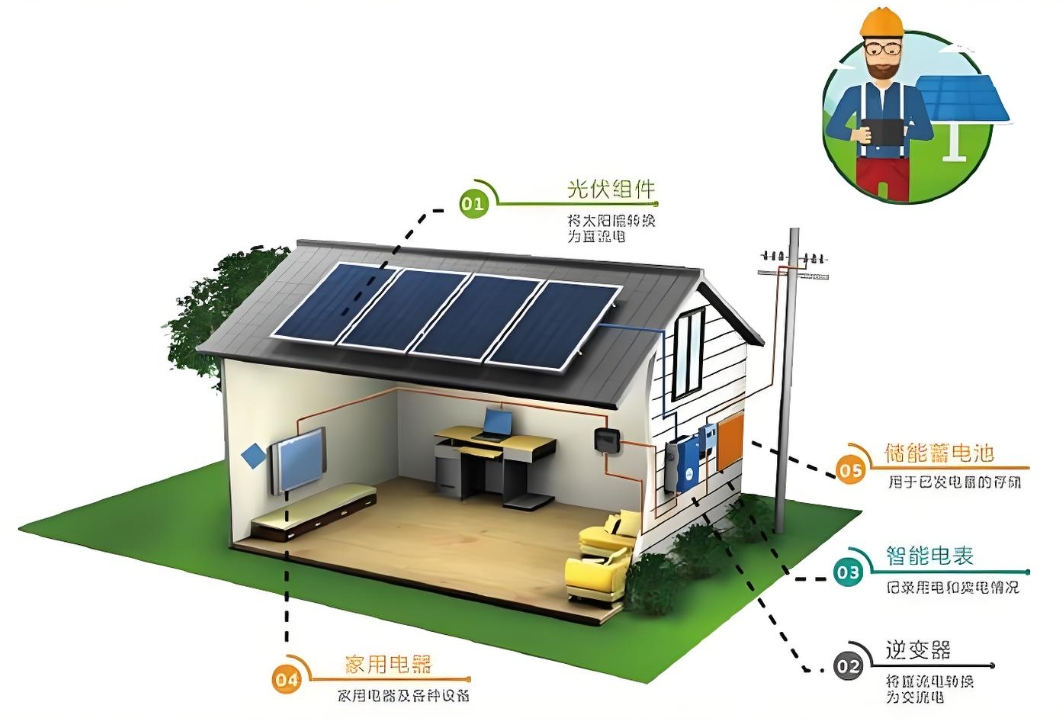
How to configure household energy storage system
Configuring a household energy storage system involves several key steps and considerations to ensure optimal performance, safety, and cost-effectiveness. Below is an expanded guide on how to configure a household energy storage system:
Step 1: Assess Household Energy Needs
Determine Daily and Peak Electricity Consumption
Begin by analyzing your household's daily and peak electricity consumption. This can be done through monitoring your electricity usage over a period of time or by consulting with a professional energy auditor. Understanding your energy needs will help you determine the appropriate size and capacity of the energy storage system.
Identify Key Loads
Identify the critical loads that need to be powered during outages or when the grid is unavailable. These may include essential appliances such as refrigerators, lighting, and heating/cooling systems. Knowing your key loads will help you size the battery capacity accordingly.
Step 2: Choose the Right Battery Technology
Evaluate Different Battery Types
There are various battery technologies available for household energy storage, including lithium-ion, lead-acid, and sodium-sulfur batteries. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of cost, energy density, cycle life, and safety.
Lithium-ion Batteries: Offer high energy density, long cycle life, and fast charging and discharging capabilities. They are generally more expensive but are becoming more affordable as technology advances.
Lead-acid Batteries: Are less expensive but have lower energy density and shorter cycle life compared to lithium-ion batteries. They are suitable for simpler energy storage systems.
Sodium-sulfur Batteries: Have high energy density and can operate at high temperatures. However, they are less common in household applications due to their complexity and cost.
Consider Battery Size and Capacity
Based on your household energy needs and the chosen battery technology, select the appropriate battery size and capacity. Ensure that the battery can store enough energy to meet your household's energy requirements during outages or when the grid is unavailable.
Step 3: Select the Right Inverter and Charge Controller
Choose an Appropriate Inverter
The inverter converts the stored energy from the battery into usable AC power for your household appliances. Choose an inverter that is compatible with your chosen battery technology and has sufficient power output to meet your household's energy needs.
Select a Charge Controller
A charge controller regulates the flow of energy from your solar panels or grid-tied system to the battery, preventing overcharging and protecting the battery from damage. Ensure that the charge controller is compatible with your chosen battery technology and has the necessary features for your application.
Step 4: Design the System Layout and Integration
Plan the System Layout
Design the layout of your energy storage system, including the placement of the battery, inverter, and charge controller. Ensure that the system is easily accessible for maintenance and that it complies with local safety regulations.
Integrate with Solar Panels (if applicable)
If you are integrating your energy storage system with solar panels, ensure that the system is designed to maximize energy harvesting and storage. This may involve optimizing the orientation and tilt of the solar panels, as well as the size and capacity of the battery.
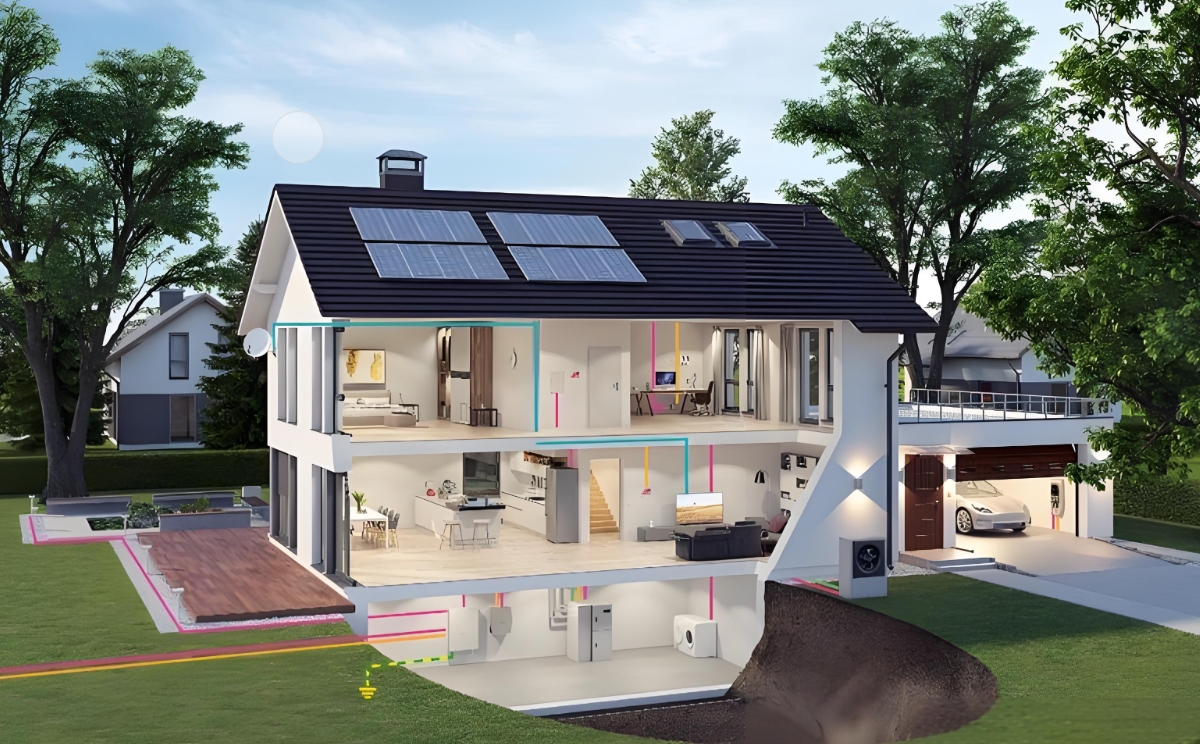

Step 5: Install and Monitor the System
Install the System
Follow the manufacturer's instructions for installing the energy storage system. Ensure that all components are properly connected and that the system is grounded for safety.
Monitor System Performance
Use a monitoring system to track the performance of your energy storage system. This will help you identify any issues or inefficiencies and make adjustments as needed.
Step 6: Consider Safety and Maintenance
Implement Safety Measures
Ensure that your energy storage system is equipped with safety features such as overcharge protection, over-discharge protection, and short-circuit protection. Regularly inspect the system for any signs of damage or wear and replace any worn-out components as needed.
Schedule Regular Maintenance
Schedule regular maintenance checks for your energy storage system to ensure its continued performance and safety. This may involve inspecting the battery, inverter, and charge controller for any signs of wear or damage, and cleaning any dust or debris that has accumulated on the components.
Conclusion
Configuring a household energy storage system involves several key steps, including assessing household energy needs, choosing the right battery technology, selecting the right inverter and charge controller, designing the system layout and integration, installing and monitoring the system, and considering safety and maintenance. By following these steps and considering the factors mentioned above, you can ensure that your household energy storage system is optimized for performance, safety, and cost-effectiveness.